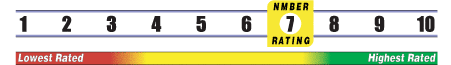
Each teabag contains: Salvia officinalis 1.5 g.
Brand name products often contain multiple ingredients. To read detailed information about each ingredient, click on the link for the individual ingredient shown above.

In 2004, Canada began regulating natural medicines as a category of products separate from foods or drugs. These products are officially recognized as "Natural Health Products." These products include vitamins, minerals, herbal preparations, homeopathic products, probiotics, fatty acids, amino acids, and other naturally derived supplements.
In order to be marketed in Canada, natural health products must be licensed. In order to be licensed in Canada, manufacturers must submit applications to Health Canada including information about uses, formulation, dosing, safety, and efficacy.
Products can be licensed based on several criteria. Some products are licensed based on historical or traditional uses. For example, if an herbal product has a history of traditional use, then that product may be acceptable for licensure. In this case, no reliable scientific evidence is required for approval.
For products with non-traditional uses, some level of scientific evidence may be required to support claimed uses. However, a high level of evidence is not necessarily required. Acceptable sources of evidence include at least one well-designed, randomized, controlled trial; well-designed, non-randomized trials; cohort and case control studies; or expert opinion reports.
Finished products licensed by Health Canada must be manufactured according to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) as outlined by Health Canada.
Below is general information about the effectiveness of the known ingredients contained in the product Phytovie Sage Tea. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
Below is general information about the safety of the known ingredients contained in the product Phytovie Sage Tea. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
LIKELY SAFE ...when used orally in amounts commonly found in foods. Sage is approved for use as a food in the United States (4912).
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used orally in medicinal doses, short-term. Common sage (Salvia officinalis) and Spanish sage (Salvia lavandulaefolia) have been used with apparent safety when taken orally in doses of 280 mg daily for up to 8 weeks (10334,10810,17177,105338). ...when used topically. Common sage (Salvia officinalis) has been used with apparent safety as a single agent or in combination products for up to one week (10437,72619,107023). ...when the essential oil is inhaled as aromatherapy, short-term (72658).
POSSIBLY UNSAFE ...when used orally in high doses or long-term (12,1304). Some species of sage, including common sage (Salvia officinalis), contain a thujone constituent that can be toxic if consumed in large enough quantities (12,1304).
PREGNANCY: LIKELY UNSAFE
when used orally.
The constituent thujone can have menstrual stimulant and abortifacient effects (19).
LACTATION: POSSIBLY UNSAFE
when used orally; sage is thought to reduce the supply of mother's milk (19).
Below is general information about the interactions of the known ingredients contained in the product Phytovie Sage Tea. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
Theoretically, sage might decrease the clinical effects of anticholinergic drugs.
|
Theoretically, sage might interfere with the clinical effects of anticonvulsant drugs.
Some species of sage can cause convulsions when consumed in large quantities (10812).
|
Theoretically, taking sage with antidiabetes drugs might increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
In patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes, common sage (Salvia officinalis) has demonstrated hypoglycemic activity (91971,103380). However, other clinical research in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes shows that common sage extract does not lower fasting blood glucose levels (105340).
|
Theoretically, sage might increase or decrease the effects of antihypertensive drugs.
Animal research suggests that common sage (Salvia officinalis) can cause prolonged blood pressure reduction (4152). However, clinical research suggests that Spanish sage (Salvia lavandulaefolia) can increase blood pressure in some people with hypertension (10334). Until more is known, use with caution.
|
Theoretically, taking sage might increase the sedative and adverse effects of benzodiazepines.
In vitro evidence suggests that certain components of common sage (Salvia officinalis) can bind to benzodiazepine receptors (72588). This effect has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, sage might have additive effects when used with cholinergic drugs.
|
Theoretically, taking sage might increase the sedative and adverse effects of CNS depressants.
Some constituents of sage have CNS depressant activity (10334).
|
Theoretically, sage might increase the levels and clinical effects of drugs metabolized by CYP2C19.
In vitro evidence suggests that aqueous extracts of sage can inhibit CYP2C19 (10848). So far, this interaction has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, sage might increase the levels and clinical effects of drugs metabolized by CYP2C9.
In vitro evidence suggests that aqueous extracts of sage can inhibit CYP2C9 (10848). So far, this interaction has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, sage might increase the levels and clinical effects of drugs metabolized by CYP2D6.
|
Theoretically, sage might decrease the levels and clinical effects of drugs metabolized by CYP2E1.
Animal research suggests that drinking common sage (Salvia officinalis) tea increases the expression of CYP2E1 (72627). So far, this interaction has not been reported in humans.
|
Theoretically, sage might increase the levels and clinical effects of drugs metabolized by CYP3A4.
|
Theoretically, sage might interfere with hormone therapy.
In vitro evidence suggests that geraniol, a constituent of Spanish sage (Salvia lavandulaefolia), exerts estrogenic activity (39572). The clinical significance of this effect is unclear.
|
Theoretically, sage might increase levels of drugs transported by P-glycoprotein.
In vitro research suggests that common sage (Salvia officinalis) can inhibit the multi-drug transporter protein, P-glycoprotein (72641). This effect has not been reported in humans.
|
Below is general information about the adverse effects of the known ingredients contained in the product Phytovie Sage Tea. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
General
...Orally, topically, and when inhaled, sage seems to be well tolerated.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Abdominal pain, agitation, diarrhea, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting.
Topically: Burning, dermatitis, pain.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: Generalized tonic-clonic seizures associated with the thujone, camphor, and/or cineol constituents.
Cardiovascular ...By inhalation, sage essential oil has been reported to increase the blood pressure of hypertensive patients (10334).
Dermatologic
...Orally, sage extract has been reported to cause acneiform skin eruptions in one patient in a clinical trial (91970).
Topically, sage leaves can cause contact dermatitis (46902,72661,72710). Sage extract can cause burning and pain (10437).
Gastrointestinal
...Orally, sage can cause nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea (10810,17177).
Topically, sage extract sprayed into the mouth and throat can cause dryness or mild burning of the throat (72619).
Neurologic/CNS ...Orally, sage can cause dizziness or agitation (10810,17177). Thujone, a constituent of common sage (Salvia officinalis), is a neurotoxin and can cause seizures (10812,12868). Camphor and cineol, constituents of common sage and Spanish sage, can also cause neurotoxicity and seizures in high doses (10334,12868). Generalized tonic-clonic seizures have been reported in adults, children, and infants after ingestion of sage oil (12868,72666).
Pulmonary/Respiratory
...Orally, sage can cause wheezing (10810,17177).
Occupational exposure to sage dust can cause reduction in ventilatory capacity and chronic respiratory impairment (72672,72682,72686).
