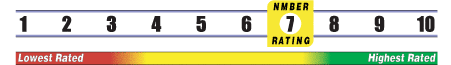
| Ingredients | Not Present |
|---|---|
|
(B. Breve )
|
Below is general information about the effectiveness of the known ingredients contained in the product B. Breve. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
Below is general information about the safety of the known ingredients contained in the product B. Breve. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
LIKELY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately. Bifidobacterium breve has been safely used alone or in combination with other probiotics in clinical trials lasting up to one year (3261,6087,11379,12769,12775,14338,14370,14371,103447,111002)(111003,111005).
CHILDREN: LIKELY SAFE
when used orally and appropriately in children of most ages.
Bifidobacterium breve has been safely used alone or in combination with other probiotics in infants and children for up to 12 months (17726,35377,92256,103449,105150,105151,107497,107598,111001)(111004,111008,111015). Cases of bacteremia have occurred rarely in children (107597). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of B. breve in preterm infants with a birth weight under 1000 grams. Cases of bacteremia have occurred rarely in preterm infants given B. breve or other probiotics (102416,111610,111612,111613,111850,111852,111853). The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued a warning about cases of serious infections caused by probiotics reported in very preterm or very low birth weight infants under 1000 grams (111610). Similarly, the American Academy of Pediatrics does not support the routine administration of probiotics to these infants due to conflicting data on safety and efficacy (111608).
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION:
There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of Bifidobacterium breve during pregnancy or lactation.
However, there are currently no reasons to expect safety concerns when used appropriately.
Below is general information about the interactions of the known ingredients contained in the product B. Breve. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
Theoretically, taking Bifidobacterium breve with antibiotic drugs might decrease the effectiveness of B. breve.
|
Below is general information about the adverse effects of the known ingredients contained in the product B. Breve. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
General
...Orally, Bifidobacterium breve seems to be well tolerated by most patients.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: There is concern that B. breve may cause bacteremia in certain patients.
Gastrointestinal ...Bloating and flatulence have been reported with probiotic use; however, these adverse effects have not been reported from ingestion of Bifidobacterium breve in particular.
Immunologic
...There have been rare cases of Bifidobacterium bacteremia related to probiotic use in critically ill infants and adults (102416,107597,107599).
In addition, cases of B. breve bacteremia have occurred in preterm infants or young children using probiotics (102416,107597). In a review of 298 term and preterm infants who were admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit of a hospital in Japan and received B. breve BBG-01 over a five-year period, bacteremia occurred in six patients (2%). Concomitant conditions included gastrointestinal perforation, food-induced enterocolitis syndrome, adhesive ileus, ileal volvulus, and aspiration pneumonia following esophageal atresia repair (107597). In one case report, B. breve BBG-01 was provided to an infant starting two days after birth and the day of surgery for an omphalocele. The infant also had bilious gastric fluid with elevated inflammatory markers. It is thought that the intestinal surgical repair might have led to the translocation of the ingested B. breve (107596).
Some cases of B. breve bacteremia do not seem to be directly related to probiotic use. There have been rare cases of B. breve bacteremia and necrotizing fasciitis in patients with type 2 diabetes. One patient had pre-existing chronic diabetic foot ulcers and the other had abscesses near the groin (111007,111011). A childhood history of frequent consumption of fermented beverages containing B. breve was thought to have resulted in B. breve in the intestinal flora of one of these patients, aged 42 years (111011). However, it is unclear if consumption of an unknown quantity of B. breve more than 20 years previously would play a role in this outcome. There is also a rare case of ventriculoperitoneal shunt B. breve infection possibly related to poor oral hygiene and dentition (111014).
