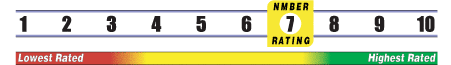
| Ingredients | Amount Per Serving |
|---|---|
|
Calories
|
10 {Calories} |
|
Calories from Fat
|
9 {Calories} |
|
Total Fat
|
1 Gram(s) |
|
Saturated Fat
|
1 Gram(s) |
| 1000 mg |
Bovine Gelatin, Glycerin, purified Water
Below is general information about the effectiveness of the known ingredients contained in the product Coconut Oil 1000 mg. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
Below is general information about the safety of the known ingredients contained in the product Coconut Oil 1000 mg. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
LIKELY SAFE ...when used orally in food amounts. Coconut oil can be safely consumed as a component of the diet (12361,17935,94452,106494). However, coconut oil should not be considered a healthy alternative to other saturated fats (94453,94643). Coconut oil contains more saturated fat than animal based fats, including lard and butter (94643). Therefore, like all saturated fats, coconut oil should be used in moderation (94453,94643). ...when used topically and appropriately. Commercial products containing coconut oil in concentrations up to 100% have been used with apparent safety. However, most research has used commercial products with concentrations up to 70% (12356,17936,17941).
POSSIBLY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately in medicinal amounts, short-term. Taking coconut oil up to 10 mL orally two or three times daily for up to 12 weeks has been used with apparent safety in clinical research (17938,17942,90615,106493).
CHILDREN: POSSIBLY SAFE
when used topically and appropriately, short-term.
Coconut oil has been used with apparent safety in children and neonates for about one month (13483,17937,90614,90616,96204,101873). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of coconut oil when taken orally in children.
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION:
There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of using coconut oil in medicinal amounts during pregnancy or lactation.
Coconut oil ingestion increases the amount of lauric acid in breast milk within 10 hours. This indicates that fatty acids from coconut oil are rapidly transferred into human breast milk following oral intake (14086). The impact of this increase in lauric acid on nursing infants is not known.
Below is general information about the interactions of the known ingredients contained in the product Coconut Oil 1000 mg. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
Below is general information about the adverse effects of the known ingredients contained in the product Coconut Oil 1000 mg. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
General
...Orally and topically, coconut oil is generally well tolerated.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Increased cholesterol levels.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
All routes of administration: Allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, in sensitive individuals.
Cardiovascular ...Due to its high saturated fat content, there has been some speculation that consuming coconut oil might increase cholesterol levels and the risk of cardiovascular disease. Several population and clinical studies have found that consuming coconut oil increases total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol in some patients (12361,14407,17935,17940,94451,94452,99103,101877,101879,106489,106494). In patients with normal to high cholesterol levels, consuming a daily diet providing 30% to 36% of calories from fat, of which 46% to 66% is from coconut oil, for 4-12 weeks increases total cholesterol by about 12-15 mg/dL, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol by about 9-12 mg/dL, and HDL cholesterol by 3-6 mg/dL when compared to a diet containing vegetable oils, especially those rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids (17935,94451,94452,101877,106489). In some cases, these cholesterol effects are similar to those seen in patients consuming a similar diet containing butter or beef fat (12361,17935,94451,99103,101879). Despite the potential effects of coconut oil on cholesterol levels, population research has not found an association with coconut oil consumption and risk of adverse cardiovascular events such as myocardial infarction or angina (14407,96205). Advise patients not to rely on coconut oil as a "healthy" alternative to other saturated fats.
Dermatologic ...In one case report, a 6-year-old child developed urticaria and hives from applying coconut oil to the skin. The child had been exposed to coconut oil consistently since 2 weeks of age, indicating sensitization over the course of regular exposure (95806). In clinical research, one patient reported localized pruritus immediately after applying a combination of coconut oil, anise oil, and ylang ylang (13483). It is unclear if this event was due to coconut oil, other ingredients, or the combination. Also, it is possible that this was an idiosyncratic event.
Gastrointestinal ...Orally, diarrhea and gastroenteritis have been reported rarely (101877).
Hepatic ...Orally, taking virgin coconut oil in the diet for 28 days modestly increased levels of liver enzymes in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). However, it is unclear if this was due to the coconut oil or to the illness (107664).
Immunologic
...Several cases of allergic reactions have been reported for patients who consumed coconut fruit.
In some of the cases, the patients were previously diagnosed with sensitivity to other tree nuts, including peanuts, so cross-sensitivity is suspected. In a separate case report, a 17-year-old male was found to be sensitized to both coconut and buckwheat, indicating a possible cross-sensitivity between the two allergens (95808). In other cases, the patients did not show sensitivity to any other allergens, so the patients were considered to have a single allergy to coconut fruit (12359,12360).
Because coconut oil is derived from coconut fruit, ingestion of coconut oil may theoretically cause allergic reactions in patients with confirmed allergy to coconut fruit. In one case report, a 6-year-old child who had previously experienced urticaria and hives from applying coconut oil to the skin experienced throat swelling and anaphylaxis after eating food containing coconut, indicating a sensitivity to both the fruit and the oil via both topical application and ingestion (95806). However, allergic reactions to coconut appear to occur significantly less often than allergies to other food items such as wheat, milk, soy, or peanut (14408).
