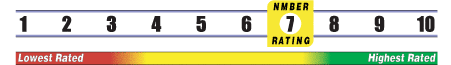
| Ingredients | Amount Per Serving |
|---|---|
|
Calories
|
5 {Calories} |
|
Total Carbohydrates
|
1 Gram(s) |
|
(Ca)
|
60 mg |
|
(root)
(1,590 mg)
(Valerian PlantPart: root Note: 1,590 mg )
|
1.59 Gram(s) |
Gelatin Note: capsule, Cellulose, Magnesium Stearate
Below is general information about the effectiveness of the known ingredients contained in the product Valerian Root. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
INSUFFICIENT RELIABLE EVIDENCE to RATE
Below is general information about the safety of the known ingredients contained in the product Valerian Root. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
LIKELY SAFE ...when used orally or intravenously and appropriately. Calcium is safe when used in appropriate doses (7555,12928,12946,95817). However, excessive doses should be avoided. The Institute of Medicine sets the daily tolerable upper intake level (UL) for calcium according to age as follows: Age 0-6 months, 1000 mg; 6-12 months, 1500 mg; 1-8 years, 2500 mg; 9-18 years, 3000 mg; 19-50 years, 2500 mg; 51+ years, 2000 mg (17506). Doses over these levels can increase the risk of side effects such as kidney stone, hypercalciuria, hypercalcemia, and milk-alkali syndrome. There has also been concern that calcium intake may be associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and coronary heart disease (CHD), including myocardial infarction (MI). Some clinical research suggests that calcium intake, often in amounts over the recommended daily intake level of 1000-1300 mg daily for adults, is associated with an increased risk of CVD, CHD, and MI (16118,17482,91350,107233). However, these studies, particularly meta-analyses, have been criticized for excluding trials in which calcium was administered with vitamin D (94137). Many of these trials also only included postmenopausal females. Other analyses report conflicting results, and have not shown that calcium intake affects the risk of CVD, CHD, or MI (92994,93533,97308,107231). Advise patients not to consume more than the recommended daily intake of 1000-1200 mg per day and to consider total calcium intake from both dietary and supplemental sources (17484). Also, advise patients taking calcium supplements to take calcium along with vitamin D (93533).
POSSIBLY UNSAFE ...when used orally in excessive doses. The National Academy of Medicine sets the daily tolerable upper intake level (UL) for calcium according to age as follows: 19-50 years, 2500 mg; 51 years and older, 2000 mg (17506). Doses over these levels can increase the risk of side effects such as kidney stones, hypercalciuria, hypercalcemia, and milk-alkali syndrome. There has also been concern that calcium intake may be associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and coronary heart disease (CHD), including myocardial infarction (MI). Some clinical research suggests that calcium intake, often in amounts over the recommended daily intake level of 1000-1300 mg daily for adults, is associated with an increased risk of CVD, CHD, and MI (16118,17482,91350,107233). However, these studies, particularly meta-analyses, have been criticized for excluding trials in which calcium was administered with vitamin D (94137). Many of these trials also only included postmenopausal females. Other analyses report conflicting results, and have not shown that calcium intake affects the risk of CVD, CHD, or MI (92994,93533,97308,107231). Advise patients to not consume more than the recommended daily intake of 1000-1200 mg per day and to consider total calcium intake from both dietary and supplemental sources (17484). Also, advise patients taking calcium supplements to take calcium along with vitamin D (93533).
CHILDREN: LIKELY SAFE
when used orally and appropriately.
Calcium is safe when used in appropriate doses (17506).
CHILDREN: POSSIBLY UNSAFE
when used orally in excessive doses.
The Institute of Medicine sets the daily tolerable upper intake level (UL) for calcium according to age as follows: 0-6 months, 1000 mg; 6-12 months, 1500 mg; 1-8 years, 2500 mg; 9-18 years, 3000 mg (17506). Doses over these levels can increase the risk of side effects such as kidney stones, hypercalciuria, hypercalcemia, and milk-alkali syndrome.
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION: LIKELY SAFE
when used orally and appropriately (945,1586,3263,3264,17506).
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends prescribing oral calcium supplementation 1.5-2 grams daily during pregnancy to those with low dietary calcium intake to prevent pre-eclampsia (97347).
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION: POSSIBLY UNSAFE
when used orally in excessive doses.
The Institute of Medicine sets the same daily tolerable upper intake level (UL) for calcium according to age independent of pregnancy status: 9-18 years, 3000 mg; 19-50 years, 2500 mg (17506). Doses over these amounts might increase the risk of neonatal hypocalcemia-induced seizures possibly caused by transient neonatal hypoparathyroidism in the setting of excessive calcium supplementation during pregnancy, especially during the third trimester. Neonatal hypocalcemia is a risk factor for neonatal seizures (97345).
LIKELY SAFE ...when used orally and appropriately, short-term. Valerian 300-600 mg daily has been safely used in clinical studies in over 12,000 patients for up to 6 weeks (2074,3484,3485,4032,15018,17577,17578,19409,96242,103221)(104010,105718). There is insufficient reliable information available about the safety of valerian when used orally for longer than 6 weeks.
CHILDREN: POSSIBLY SAFE
when used orally and appropriately, short-term.
Valerian 160-320 mg has been used with apparent safety in children under 12 years of age for 4-8 weeks (14416).
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION:
Insufficient reliable information available; avoid using.
Below is general information about the interactions of the known ingredients contained in the product Valerian Root. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
Calcium citrate might increase aluminum absorption and toxicity. Other types of calcium do not increase aluminum absorption.
Calcium citrate can increase the absorption of aluminum when taken with aluminum hydroxide. The increase in aluminum levels may become toxic, particularly in individuals with kidney disease (21631). However, the effect of calcium citrate on aluminum absorption is due to the citrate anion rather than calcium cation. Calcium acetate does not appear to increase aluminum absorption (93006).
|
Calcium reduces the absorption of bisphosphonates.
Advise patients to take bisphosphonates at least 30 minutes before calcium, but preferably at a different time of day. Calcium supplements decrease absorption of bisphosphonates (12937).
|
Taking calcipotriene with calcium might increase the risk for hypercalcemia.
Calcipotriene is a vitamin D analog used topically for psoriasis. It can be absorbed in sufficient amounts to cause systemic effects, including hypercalcemia (12938). Theoretically, combining calcipotriene with calcium supplements might increase the risk of hypercalcemia.
|
Intravenous calcium may decrease the effects of calcium channel blockers; oral calcium is unlikely to have this effect.
Intravenous calcium is used to decrease the effects of calcium channel blockers in the management of overdose. Intravenous calcium gluconate has been used before intravenous verapamil (Isoptin) to prevent or reduce the hypotensive effects without affecting the antiarrhythmic effects (6124). But there is no evidence that dietary or supplemental calcium when taken orally interacts with calcium channel blockers (12939,12947).
|
Co-administration of intravenous calcium and ceftriaxone can result in precipitation of a ceftriaxone-calcium salt in the lungs and kidneys.
Avoid administering intravenous calcium in any form, such as parenteral nutrition or Lactated Ringers, within 48 hours of intravenous ceftriaxone. Case reports in neonates show that administering intravenous ceftriaxone and calcium can result in precipitation of a ceftriaxone-calcium salt in the lungs and kidneys. In several cases, neonates have died as a result of this interaction (15794,21632). So far there are no reports in adults; however, there is still concern that this interaction might occur in adults.
|
Using intravenous calcium with digoxin might increase the risk of fatal cardiac arrhythmias.
|
Theoretically, calcium may reduce the therapeutic effects of diltiazem.
Hypercalcemia can reduce the effectiveness of verapamil in atrial fibrillation (10574). Theoretically, calcium might increase this risk of hypercalcemia and reduce the effectiveness of diltiazem.
|
Calcium seems to reduce levels of dolutegravir.
Advise patients to take dolutegravir either 2 hours before or 6 hours after taking calcium supplements. Pharmacokinetic research suggests that taking calcium carbonate 1200 mg concomitantly with dolutegravir 50 mg reduces plasma levels of dolutegravir by almost 40%. Calcium appears to decrease levels of dolutegravir through chelation (93578).
|
Calcium seems to reduce levels of elvitegravir.
Advise patients to take elvitegravir either 2 hours before or 2 hours after taking calcium supplements. Pharmacokinetic research suggests that taking calcium along with elvitegravir can reduce blood levels of elvitegravir through chelation (94166).
|
Calcium seems to reduce the absorption and effectiveness of levothyroxine.
|
Theoretically, concomitant use of calcium and lithium may increase this risk of hypercalcemia.
Clinical research suggests that long-term use of lithium may cause hypercalcemia in 10% to 60% of patients (38953). Theoretically, concomitant use of lithium and calcium supplements may further increase this risk.
|
Calcium seems to reduce the absorption of quinolone antibiotics.
|
Calcium may reduce levels of raltegravir.
Pharmacokinetic research shows that taking a single dose of calcium carbonate 3000 mg along with raltegravir 400 mg twice daily modestly decreases the mean area under the curve of raltegravir, but the decrease does not necessitate a dose adjustment of raltegravir (94164). However, a case of elevated HIV-1 RNA levels and documented resistance to raltegravir has been reported for a patient taking calcium carbonate 1 gram three times daily plus vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) 400 IU three times daily in combination with raltegravir 400 mg twice daily for 11 months. It is thought that calcium reduced raltegravir levels by chelation, leading to treatment failure (94165).
|
Calcium seems to reduce the absorption of sotalol.
Advise patients to separate doses by at least 2 hours before or 4-6 hours after calcium. Calcium appears to reduce the absorption of sotalol, probably by forming insoluble complexes (10018).
|
Calcium seems to reduce the absorption of tetracycline antibiotics.
Advise patients to take oral tetracyclines at least 2 hours before, or 4-6 hours after calcium supplements. Taking calcium at the same time as oral tetracyclines can reduce tetracycline absorption. Calcium binds to tetracyclines in the gut (1843).
|
Taking calcium along with thiazides might increase the risk of hypercalcemia and renal failure.
Thiazides reduce calcium excretion by the kidneys (1902). Using thiazides along with moderately large amounts of calcium carbonate increases the risk of milk-alkali syndrome (hypercalcemia, metabolic alkalosis, renal failure). Patients may need to have their serum calcium levels and/or parathyroid function monitored regularly.
|
Theoretically, calcium may reduce the therapeutic effects of verapamil.
Hypercalcemia can reduce the effectiveness of verapamil in atrial fibrillation (10574). Theoretically, use of calcium supplements may increase this risk of hypercalcemia and reduce the effectiveness of verapamil.
|
Valerian can have additive sedative effects when used concomitantly with alcohol.
Valerian has sedative effects (9894). Theoretically, valerian might have an additive sedative effect when combined with alcohol. Excessive sedation has been reported in an alcohol-abusing individual who took valerian and Gingko biloba (19426). However, the potential interaction between valerian and alcohol has been disputed in other research. Limited evidence suggests that a combination of valerian 160 mg and lemon balm 80 mg (Euvegal) does not cause further deterioration in reaction ability and reaction rate when taken with alcohol as compared to the effects of alcohol alone (19427).
|
Valerian can have additive sedative effects when used with alprazolam. Also, valerian in high doses might modestly increase alprazolam levels, though this is not likely to be clinically significant.
Valerian has sedative effects (9894). Theoretically, valerian might cause additive sedation when combined with alprazolam. Also, a small pharmacokinetic study shows that taking valerian extract 1000 mg daily (providing 11 mg valerenic acid) might increase alprazolam levels by about 19%. This might be due to valerian's mild inhibition of cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) (13014). Despite being statistically significant, this increase is not likely to be clinically significant.
|
Valerian can have additive sedative effects when used concomitantly with CNS depressant drugs.
|
Valerian does not seem to have a clinically relevant effect on levels of drugs metabolized by CYP2D6.
Although some in vitro evidence suggests that valerian affects CYP2D6, clinical pharmacokinetic (PK) studies show that valerian is unlikely to affect the CYP2D6 enzyme (13014,13536,19430,19431). In one PK study, taking valerian 1000 mg (providing about 11 mg valerenic acid) nightly for 14 days did not affect the metabolism of dextromethorphan, a CYP2D6 substrate. In another PK study, taking valerian 125 mg three times daily for 28 days did not affect metabolism of debrisoquine, an accepted CYP2D6 probe-substrate (13014,13536).
|
Valerian does not seem to have a clinically relevant effect on levels of drugs metabolized by CYP3A4.
Although some in vitro evidence suggests that valerian extract might inhibit or induce CYP3A4, clinical pharmacokinetic (PK) studies show that valerian does not have a clinically significant effect on the CYP3A4 enzyme (6450,12214,13014,13536,19431). In one PK study, taking valerian 125 mg three times daily for 28 days did not affect metabolism of midazolam, an accepted CYP3A4 probe-substrate. In another PK study, taking valerian 1000 mg (providing about 11 mg valerenic acid) nightly for 14 days modestly increases levels of alprazolam, a CYP3A4 substrate, suggesting mild inhibition of CYP3A4 (13014,13536). However, this mild inhibition is unlikely to be clinically relevant.
|
Valerian might weakly inhibit glucuronidation and increase concentrations of drugs metabolized by UGT1A1 and UGT2B7.
In vitro research shows that methanolic valerian extract and valerenic acid might competitively inhibit UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 1A1 (UGT1A1) and UGT2B7 (81685).
|
Below is general information about the adverse effects of the known ingredients contained in the product Valerian Root. Some ingredients may not be listed. This information does NOT represent a recommendation for or a test of this specific product as a whole.
General
...Orally and intravenously, calcium is well-tolerated when used appropriately.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Belching, constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, and stomach upset.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: Case reports have raised concerns about calciphylaxis and kidney stones.
Cardiovascular
...There has been concern that calcium intake may be associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and coronary heart disease (CHD), including myocardial infarction (MI).
Some clinical research suggests that calcium intake, often in amounts over the recommended daily intake level of 1000-1300 mg daily for adults, is associated with an increased risk of CVD, CHD, and MI (16118,17482,91350,107233). However, these results, particularly meta-analyses, have been criticized for excluding trials in which calcium was administered with vitamin D (94137). Many of these trials also only included postmenopausal females. Other analyses report conflicting results, and have not shown that calcium intake affects the risk of CVD, CHD, or MI (92994,93533,97308,107231). Reasons for these discrepancies are not entirely clear. It may relate to whether calcium is taken as monotherapy or in combination with vitamin D. When taken with vitamin D, which is commonly recommended, calcium supplementation does not appear to be associated with an increased risk of CVD, CHD, or MI (93533,107231). Also, the association between calcium supplementation and CVD, CHD, or MI risk may be influenced by the amount of calcium consumed as part of the diet. Supplementation with calcium may be associated with an increased risk of MI in people with dietary calcium intake above 805 mg daily, but not in those with dietary calcium intake below 805 mg daily (17482). To minimize the possible risk of CVD, CHD, or MI, advise patients not to consume more than the recommended daily intake of 1000-1200 mg and to consider total calcium intake from both dietary and supplemental sources (17484). While dietary intake of calcium is preferred over supplemental intake, advise patients who require calcium supplements to take calcium along with vitamin D, as this combination does not appear to be associated with an increased risk of MI (93533).
Rarely, calcium intake can increase the risk of calciphylaxis, which usually occurs in patients with kidney failure. Calciphylaxis is the deposition of calcium phosphate in arterioles, which causes skin ulcers and skin necrosis. In a case report, a 64-year-old female with a history of neck fracture, sepsis, and ischemic colitis presented with painful leg ulcers due to calciphylaxis. She discontinued calcium and vitamin D supplementation and was treated with sodium thiosulfate and supportive care (95816).
Gastrointestinal ...Orally, calcium can cause belching, flatulence, nausea, gastrointestinal discomfort, and diarrhea (1824,1843,12950,38803). Although constipation is frequently cited as an adverse effect of calcium, there is no scientific substantiation of this side effect (1824,1843,1844,1845,12950,38978). Calcium carbonate has been reported to cause acid rebound, but this is controversial (12935,12936).
Oncologic ...There is some concern that very high doses of calcium might increase the risk of prostate cancer. Some epidemiological evidence suggests that consuming over 2000 mg/day of dietary calcium might increase the risk for prostate cancer (4825,12949). Additional research suggests that calcium intake over 1500 mg/day might increase the risk of advanced prostate cancer and prostate cancer mortality (14132). Consumption of dairy products has also been weakly linked to a small increase in prostate cancer risk (98894). However, contradictory research suggests no association between dietary intake of calcium and overall prostate cancer risk (14131,14132,104630). More evidence is needed to determine the effect of calcium, if any, on prostate cancer risk.
Renal ...Kidney stones have been reported in individuals taking calcium carbonate 1500 mg daily in combination with vitamin D 2000 IU daily for 4 years (93943).
General
...Orally, valerian is generally well-tolerated.
Most Common Adverse Effects:
Orally: Dizziness, drowsiness, and mental slowness. Other reported side effects include headache, gastrointestinal upset, excitability, and vivid dreams. When used chronically and abruptly stopped, symptoms of withdrawal such as tachycardia, anxiety, irritability, and insomnia might occur. Advise patients to taper doses slowly after extended use.
Serious Adverse Effects (Rare):
Orally: Several case reports raise concerns about hepatotoxicity after the use of valerian and valerian-containing multi-ingredient dietary supplements. Withdrawal from chronic valerian use has been associated with cases of cardiac failure and hallucinations.
Cardiovascular ...When used orally in high doses for an extended period of time, valerian withdrawal has been associated with tachycardia and high output cardiac failure in one patient with a history of coronary artery disease (3487). Chest tightness has been reported for an 18-year-old female who took 40-50 capsules containing valerian 470 mg/capsule (659). A case of severe hypotension, suspected to be due to vasodilation, hypocalcemia, and hypokalemia, has been reported for a patient who injected an unknown quantity of a crude tap water extract of raw valerian root (81734).
Dermatologic ...Orally, valerian might rarely cause a rash. A case of valerian-related rash that resolved after valerian root discontinuation was reported in clinical research (19422).
Gastrointestinal ...Orally, valerian has been associated with increased incidence of gastrointestinal problems including diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain (15046,19406,19407,19422,110712). In one individual, taking 20 times the normal dose caused abdominal cramping (659).
Hepatic
...There have been several case reports of hepatotoxicity associated with the use of multi-ingredient oral preparations containing valerian (8243,96241).
In one case report, a 57-year-old man presented with acute hepatitis after consuming a cold and flu remedy containing valerian 2 grams for 3 days; the remedy also contained white willow, elderberry, and horseradish. Although the use of the cold and flu remedy was discontinued one month prior to symptom presentation, the acute hepatitis was attributed to valerian root and treated with steroids (96241). It is possible, however, that some of these preparations may have been adulterated with hepatotoxic agents (8243).
Hepatotoxicity involving long-term use of single-ingredient valerian preparations has also been reported (3484,17578). Also, a case of a 38-year-old female with liver insufficiency and cirrhosis of a vascular parenchymal nature who developed hepatotoxic symptoms following valerian and ethyl-alcohol abuse has been reported (81697). Symptoms resolved and laboratory values normalized following intense plasmapheresis treatment. Another case of acute hepatitis characterized by elevated aminotransferases, mild fibrosis, and liver inflammation has been reported for a 50-year-old female who consumed valerian root extract 5 mL three times weekly along with 10 tablets of viamine, a product containing dry valerian extract 125 mg/tablet, for 2 months (81696). Because a variety of doses were used in these cases, and many people have used higher doses safely, these hepatotoxic reactions might have been idiosyncratic. Tell patients the long-term effect of valerian on liver function is unknown.
Musculoskeletal ...In a case report, combined intake of valerian and passionflower caused throbbing and muscular fatigue when taken concomitantly with lorazepam (19429).
Neurologic/CNS ...Orally, valerian might cause dizziness, headaches, fatigue, sleepiness, and mental dullness (3484,17578,19411,19422,81723,89407). The severity of adverse effects appears to increase with higher doses (19411). However, taking valerian extracts in doses up to 1800 mg does not appear to significantly affect mood or psychomotor performance (10424,15044). Valerian does not usually have a negative impact on reaction time, alertness, and concentration the morning after intake (2074,8296). Clinical research shows that a single dose of valerian root 1600 mg is not associated with any changes in sleepiness, reaction time, or driving performance within 1-4 hours after intake (96240). More serious side effects may occur when valerian is taken at higher doses. In one individual, 20 times the normal dose caused tremor of the hand and foot and lightheadedness (659). In a case report, combined intake of valerian and passionflower caused shaking of the hands and dizziness when taken concomitantly with lorazepam (19429).
Psychiatric ...Orally, valerian has been associate with reports of restlessness, excitability, uneasiness, agitation, and vivid dreams (3484,17578,19411,19422). Chronic use and rapid cessation can lead to withdrawal syndrome with symptoms of agitation, insomnia, and hallucinations (104003). There appears to be a trend towards increased severity of adverse effects with higher doses (19411). A case of acute hypomania has been reported for a 21-year-old female patient who took a valerian decoction in water each night for one month to treat subclinical anxiety. Symptoms included euphoric mood, rapid speech, and increased sociability and sexual interest. Following cessation of valerian use and treatment with quetiapine 100 mg daily for two weeks, the patient recovered (89405). In another case report, an 85-year-old male with mild cognitive impairment, major depression, anxiety, and chronic kidney disease presented to the emergency department with hallucinations, confusion, and agitation thought to be due to abrupt cessation after taking valerian 600 mg daily for about 6 months. The symptoms resolved in about 5 days (104003).
